Hardware checks
If you are using the switch in your LAN configuration check its hardware details as well to see if it can handle 1GB speeds.
The next step is network cables, some cables are not designed and their copper can not transfer 1GB of flow, check to see if your cable is classified for the desired speed. To visually check cables do the following
- Check both connection jacks to see if it has any loose or frayed wires. If any of the wires are loose, it can be the cause of the performance issue. You should replace the cable if you discover damage to the connectors.
- Inspect the entire length of the cable and check if the harness shows any clear signs of damage. A bent or damaged cable can reduce the amount of information it’s capable of transferring between the PC and LAN router. If you find any damage to the cable, replace it to restore your network speed.
- Is the cable capable of transferring 1GB speeds? Different network cables support different network speeds. A Cat-5 cable will only provide 100MB transfers, while a Cat-5e or Cat-6 can support up to 10GB transfers. Check the cable’s labels to make sure you are using a Cat-5e or higher-rated data cable.
Now when the hardware issue is out of the way we can focus a little more on the software part.
Let's try the first easy solution, run Windows built-in troubleshooter
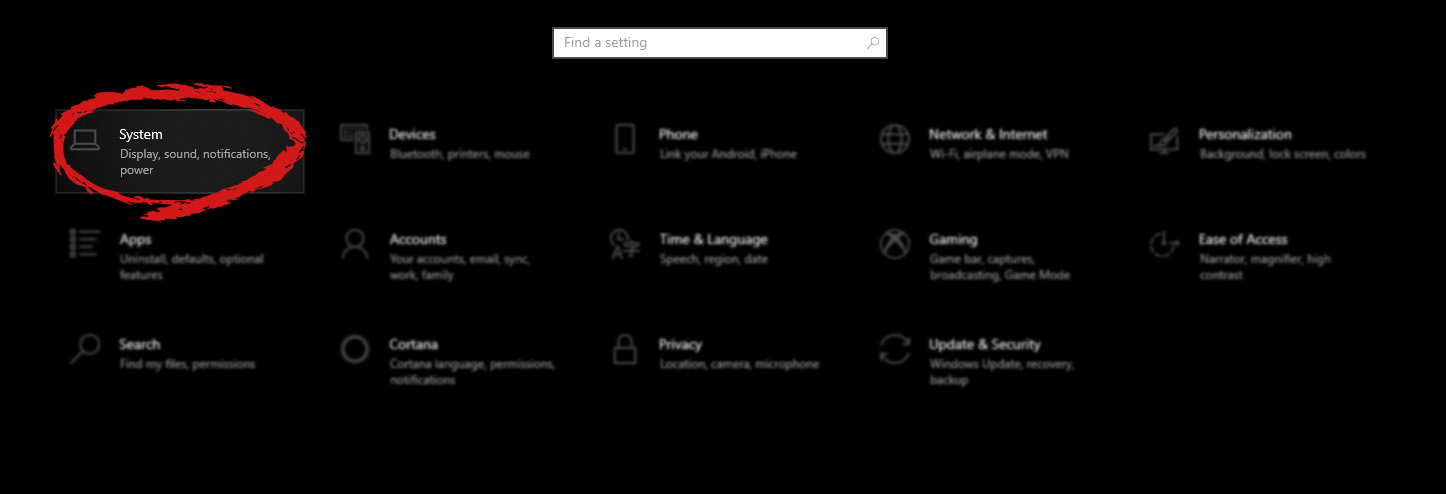
- Click the Windows button and type Control Panel. Then select the top result.
- If your Control Panel shows the Category View, change it to display Small Icons instead.
- From the list of available applications, select Network and Sharing Center.
- In your Network and Sharing Center, you can see the active network, set up a new network connection, troubleshoot problems, or change your adapter settings. Before making changes to your device properties, you can let Windows run a troubleshooter on your adapters to see if it can automatically fix your connection issues.
- Click on Troubleshoot Problems from the Change Your Network Settings section.
- In the Troubleshooter Application, scroll down and find the Network Adapter option.
- Click on Run Troubleshooter to let Windows check your network adapter’s configuration for any issues.
- Select the Ethernet Adapter you’re currently using from the list and click Next to proceed.
- Wait for the process to complete and check the results. If Windows detects any issues, it will recommend a fix. However, if the configuration of your network adapters does not have any problems, you’ll see a message that Windows couldn’t detect any problems.
- If there are any issues with the cable, the troubleshooter will detect the connection issue and request you replace the cable and connect it to your PC.
- It can occur that even after inspecting the cable and you didn’t find any visible damage on the housing or connectors, it could still be faulty. Replace the cable with a new one and rerun the troubleshooter to see if the cable is working as required.
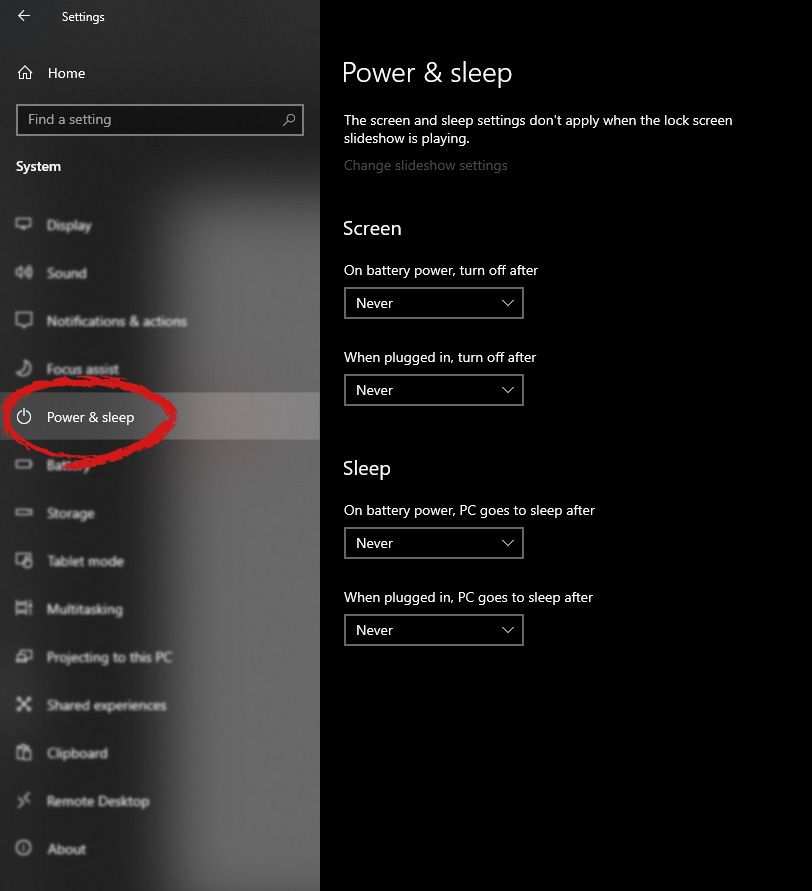
If the troubleshooter finished and you received a Windows Couldn’t Detect Any Issues result, you’ll need to verify your adapter’s speed settings.
- In your Network and Sharing Center, select the Change Adapter Settings option from the left menu.
- On the list of adapters, choose the one you’re using and click the Right Mouse Button to open the context menu.
- Select Properties from the Context Menu to access your adapter’s settings.
- On the Ethernet Properties window, you can enable or disable different features and install additional protocols. To change the device settings, click on Configure to continue.
- This will open the Device Controller Properties window where you can check the status, make changes to the settings, find out information about the driver, or check historical events on the device. Select the Advanced tab to access the device settings.
- On the Advanced tab, locate the Speed and Duplex setting.
- The Auto-Negotiation option may cause network performance issues on certain Ethernet adapters and routers. The setting allows your adapter to change the speed settings according to the LAN configuration you connect to your PC. If you connect to different LAN networks regularly with different speeds, it can occur that the setting doesn’t update from 100MB to 1GB while switching.
- Change the Value to match the network speed of the LAN you’re connecting to your PC and use the manual speed setting.
- Click OK to apply the setting and test your network performance. If your adapter doesn’t have the 1GB setting available but you know the rating should go up to that speed, it could indicate that you aren’t using the right driver for the device.
If you don’t have the setting available or the device still only provides 100MB speeds after changing the Speed setting to a manual value, you may have to update the driver for the device.
- On the Ethernet Properties Window, once again click on Configure to access the Device Properties Window. Then select the Driver Tab to access your driver details.
- Select Update Driver from the available options.
- On the Update Driver window, select the option to let Windows Search Automatically for Updated Driver Software.
- Windows will connect to the internet and search for the latest drivers online. If a newer driver exists, Windows will download and install the driver for you. If you’re using the latest driver, Windows will inform you that no updated drivers are available.
 العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা 简体中文
简体中文 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית हिन्दी
हिन्दी Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Português
Português ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Русский
Русский Español
Español So far I believe each person on this planet has at least heard of Marvel superhero movies, perhaps even watched a few of them, and no wonder. Movies are spawning now over 20 titles and they are not really released as events described in them.
So far I believe each person on this planet has at least heard of Marvel superhero movies, perhaps even watched a few of them, and no wonder. Movies are spawning now over 20 titles and they are not really released as events described in them.
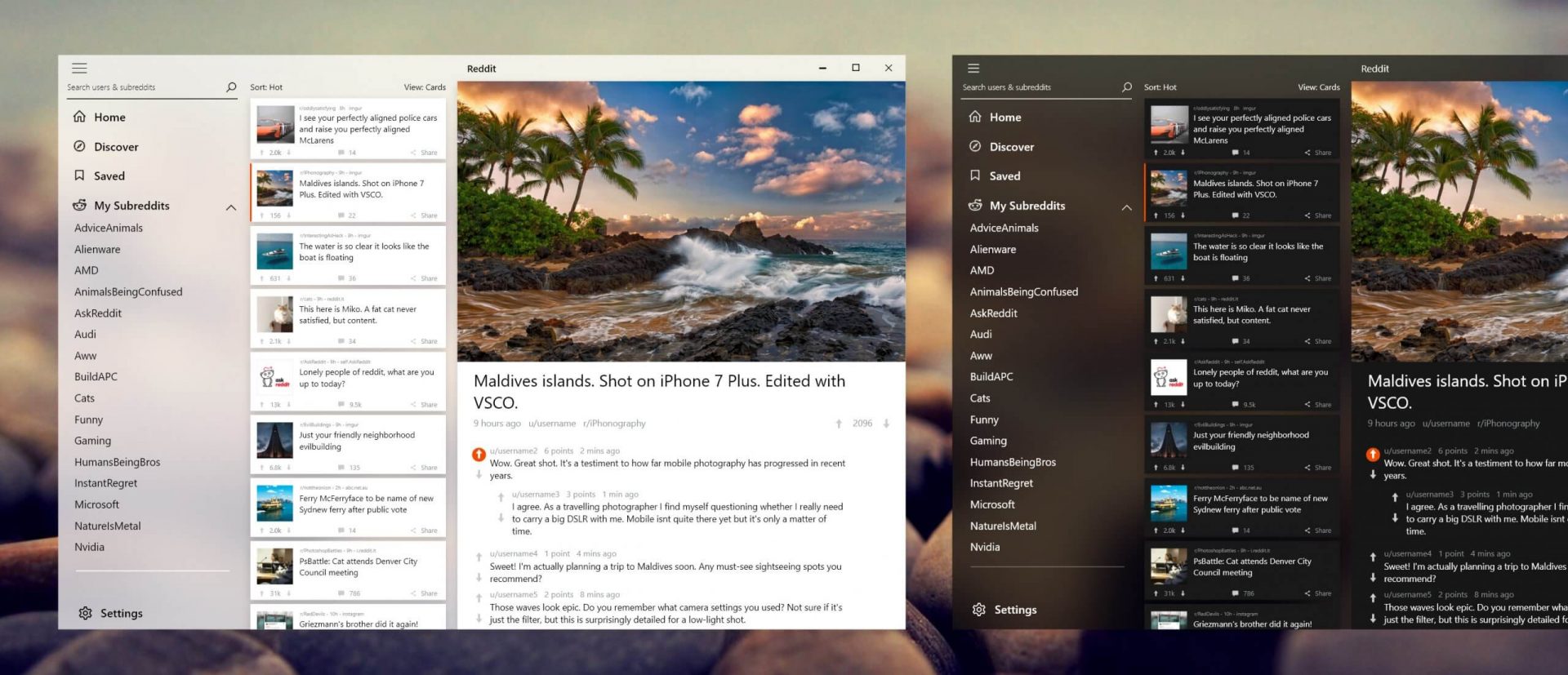 Reddit is one of the most popular websites in the world and how Microsoft is opening doors to everyone in its new store Reddit took a logical step and made a Progressive web application and placed it in it.
Being a Progressive web app makes it more familiar and feels like a home experience using it for a lot of Reddit users.
Reddit itself has a large community and active topics discussions all the time about anything. Bringing it to Windows as an application is, in my opinion, a great move since as an application it is independent, more light-weighted, and offering some other advantages specifically tied to being a standalone windows application.
Everyone familiar with and using the Reddit website will feel right at home in this app and you can start using it right away.
Reddit is one of the most popular websites in the world and how Microsoft is opening doors to everyone in its new store Reddit took a logical step and made a Progressive web application and placed it in it.
Being a Progressive web app makes it more familiar and feels like a home experience using it for a lot of Reddit users.
Reddit itself has a large community and active topics discussions all the time about anything. Bringing it to Windows as an application is, in my opinion, a great move since as an application it is independent, more light-weighted, and offering some other advantages specifically tied to being a standalone windows application.
Everyone familiar with and using the Reddit website will feel right at home in this app and you can start using it right away. 
 You can it here:
You can it here: