Having an eMail in today's modern world is no longer a privilege or being geeky, it has surely become a necessity. From Facebook to LinkedIn or Steam many services today require you to have an account in order to use them, and in order to create an account, you need working eMail.
That being said many people today have several eMail accounts, one for social media, one for work, maybe even one for very close friends and family. How creating eMail today is completely free we might end up with several eMail accounts.
eMail clients have also evolved much since their first days and became more than just applications for receiving eMails, today they can take various different tasks having additional features built into them like calendar, batch eMail processing, etc.
Taking all of said into account I am presenting to you within my personal opinion some of the best eMail clients starting with free ones.
Best free eMail clients
Google Gmail
https://gmail.com
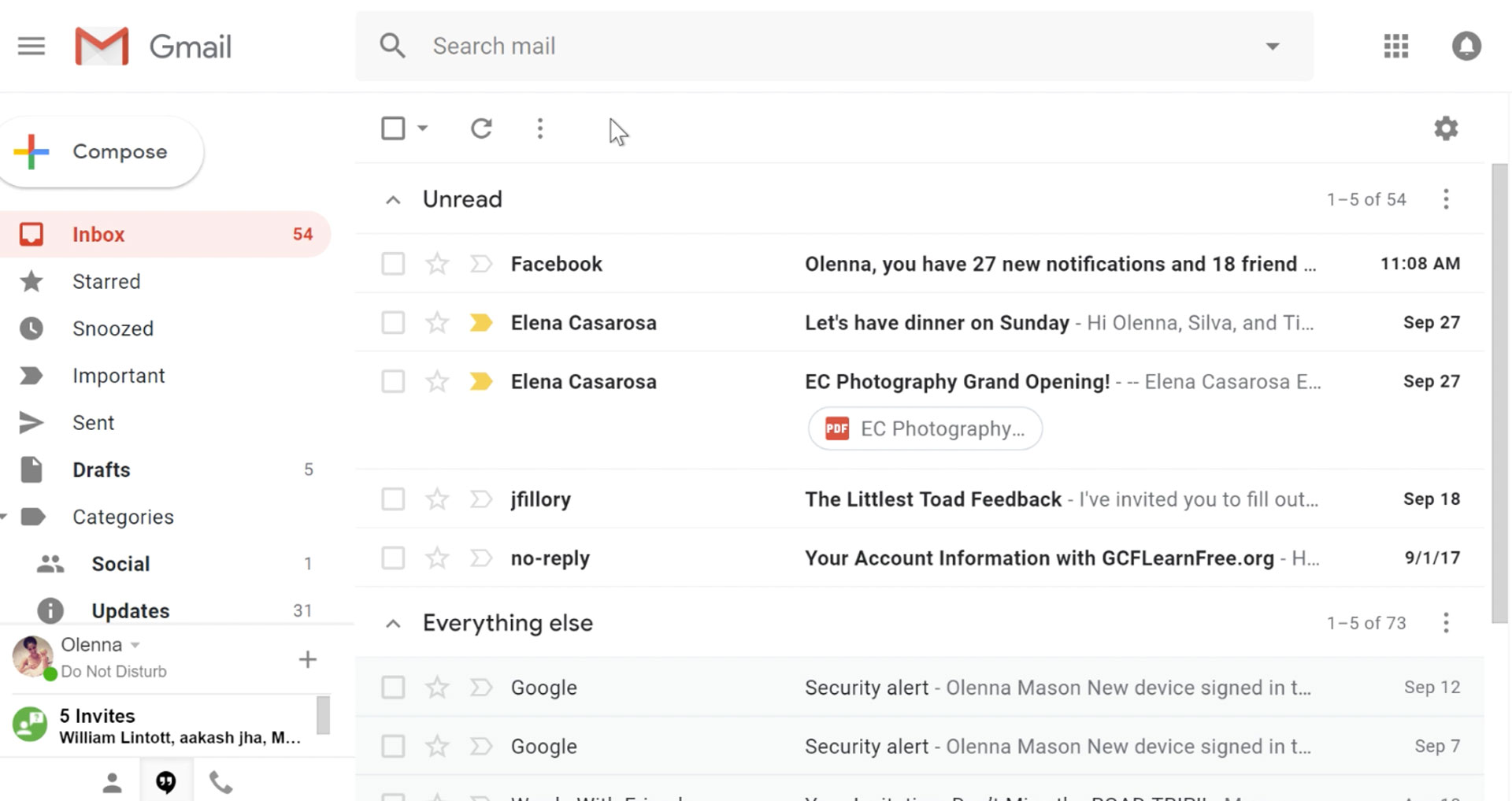
It would be very difficult to even start a free eMail list without mentioning Google's Gmail. Introduced all the way back in 2004 as an invite-only service it became over time the most popular email platform largely due to the fact Google is offering free eMail accounts.
There are a lot of good things to be said about Gmail itself, most of the area is clutter-free and the largest space is reserved for eMail itself letting users focus on what is important. WEB client itself means that you do not need to have any application installed on your device, altho via Google chrome, you can use Gmail offline offering you flexibility if needed.
The ability to connect and manage other accounts like Outlook, Yahoo, etc is just making Gmail even more attractive, and the snooze feature is a really neat little detail that will pause eMail notifications if you need to focus on other things.
Lack of organizing messages into folders is a little confusing since Gmail offers its own unique label system but sometimes I need to have old reliable save eMail to folder.
All in all, Gmail is a great service and it offers a great eMail on the go experience.
Mail eMail client
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/p/mail-and-calendar/
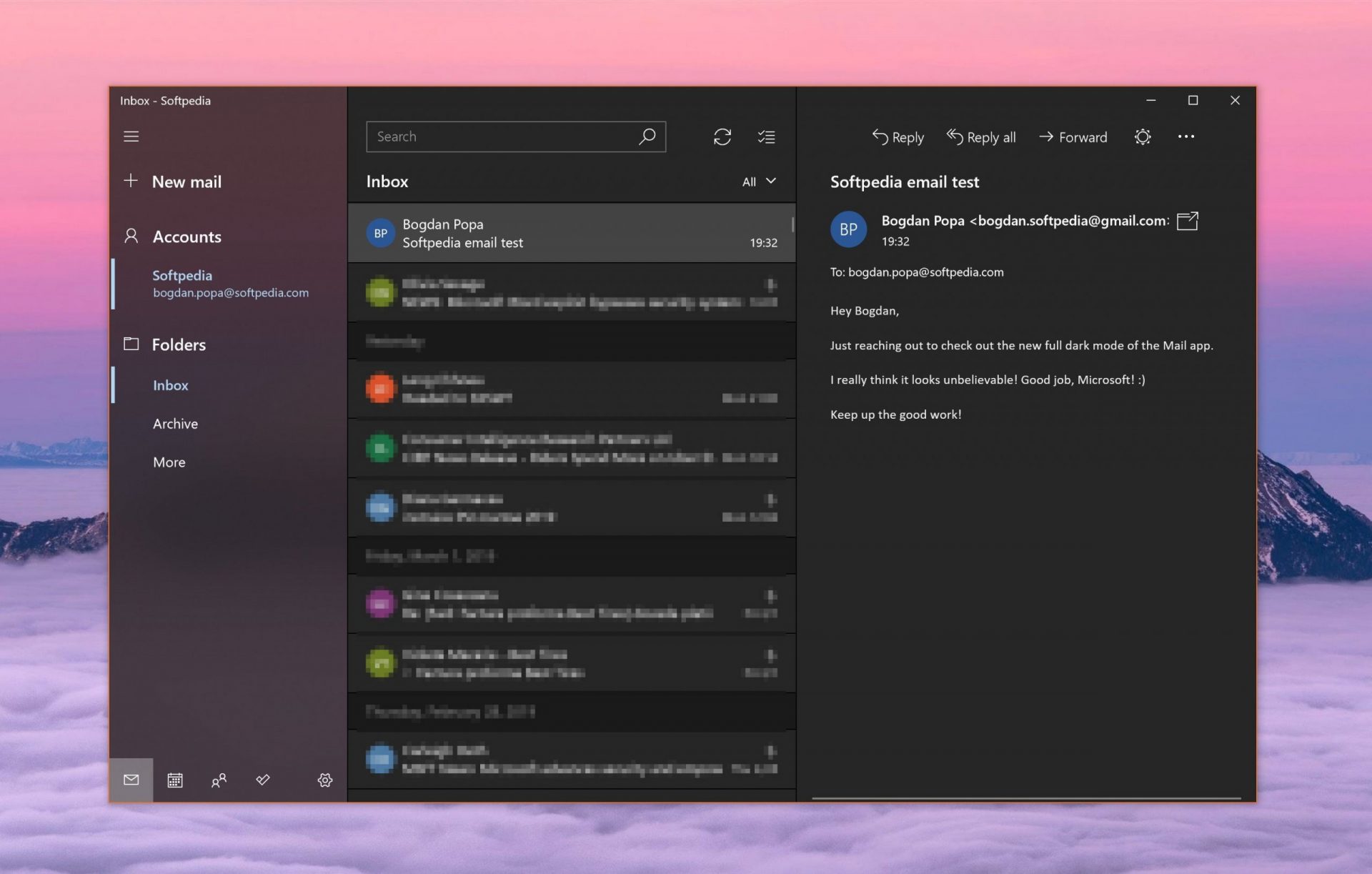
Free Windows eMail client simply called Mail is what was once outlook express. Mail itself has the ability to work with other popular accounts like Google Gmail account, Yahoo, iCloud etc. How it comes with Windows OS and it integrates very well with Microsoft Calendar, this eMail client is for many the first choice.
On the negative side, I might say this is a strip-down version of Outlook which is paid solution so some features are missing if we would compare the two.
Overall, a simple and nice eMail client worth your time, especially if you are on the Windows platform.
Mozilla Thunderbird
https://www.thunderbird.net
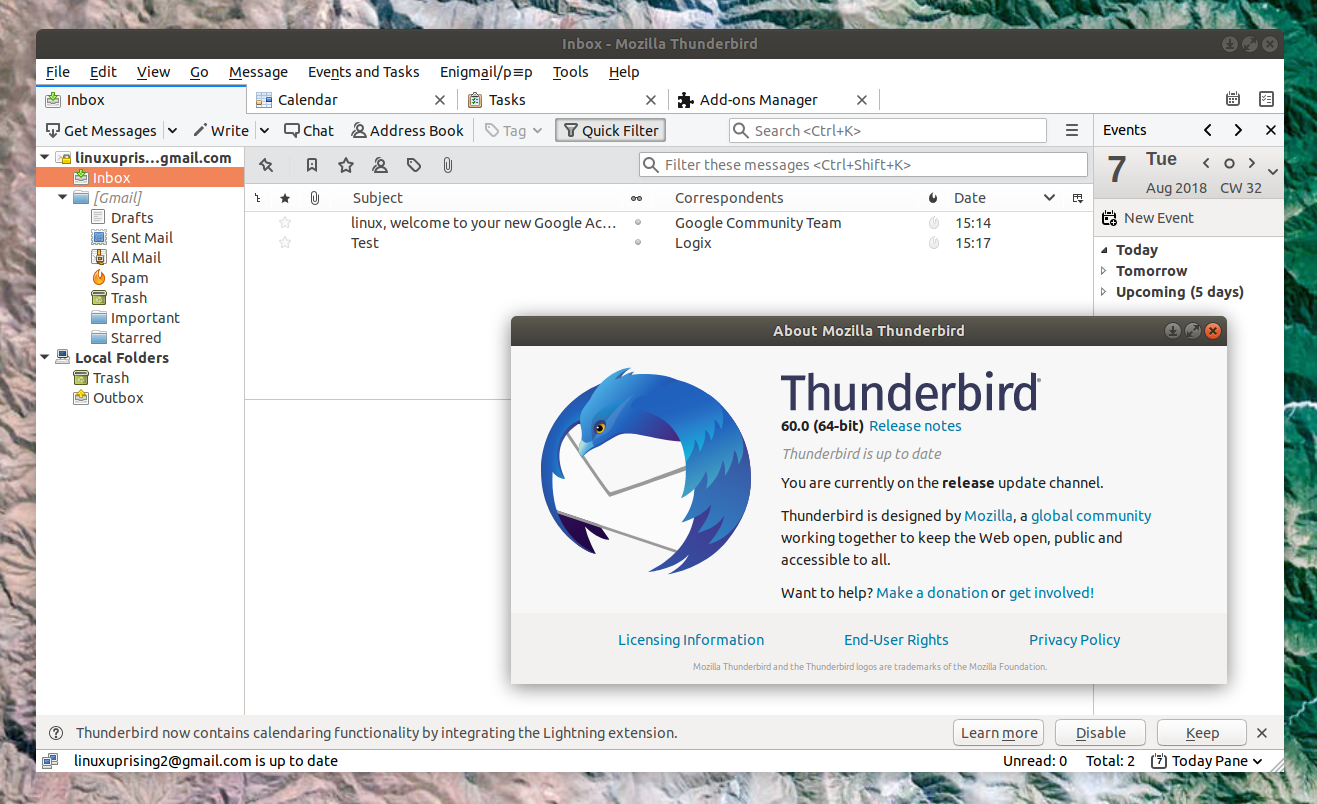
Great eMail client matching in functions against paid and premium solutions of big tech companies. Fueled with plenty of customization options and reskinning ones this eMail client offers a lot for its free price tag.
It is also fueled by Mozilla community focusing on privacy and security. It can work with any mail service and it is lightweight with a clean look, altho the look itself can be heavily customized.
The bad side is that client itself relies on email services to provide cloud-based emails, so if you are receiving your email via a service that does not have a cloud-based service in itself all of your received emails will be locked to the computer where you have received them. Also customizing it can be sometimes a little too technical for the average computer user.
All in all, Thunderbird is one great eMail client and it would be a shame not to use it because of its technical side, if you need a reliable and secure eMail client on a single machine, look no further than Thunderbird.
Paid eMail clients
Microsoft Outlook
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/
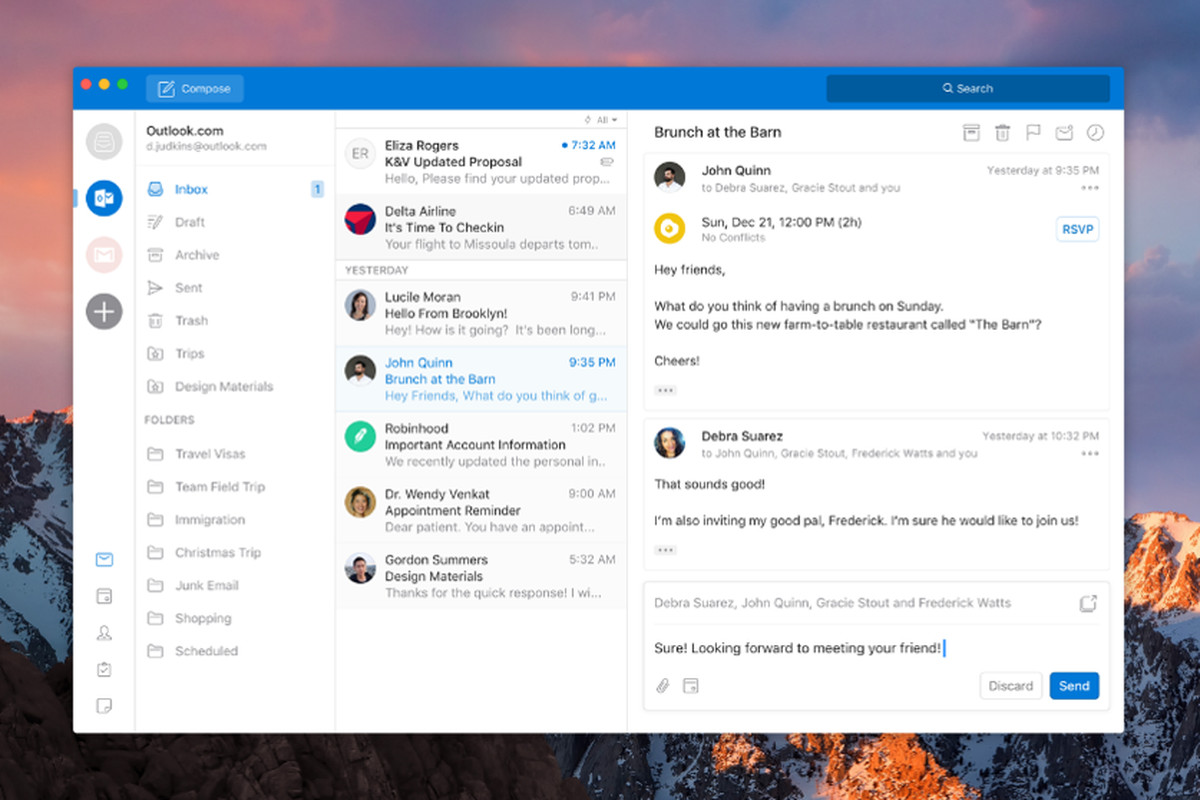
Outlook comes as a part of the Microsoft Office suite and as one of the oldest eMail clients, it is still widely popular and adopted through many users and businesses. It has tight integration with all Microsoft services and full integration with Calendar making it one of the if not the best eMail client out there.
Outlook also has a free online service completely free for personal use as well.
The downside is that you can not get it as a separate product if you want a business version other than as a part of the Office suite.
The final verdict would be that this is perhaps the best eMail client out but the big downside is that there is no desktop version outside the Office suite.
eM Client
https://www.emclient.com/
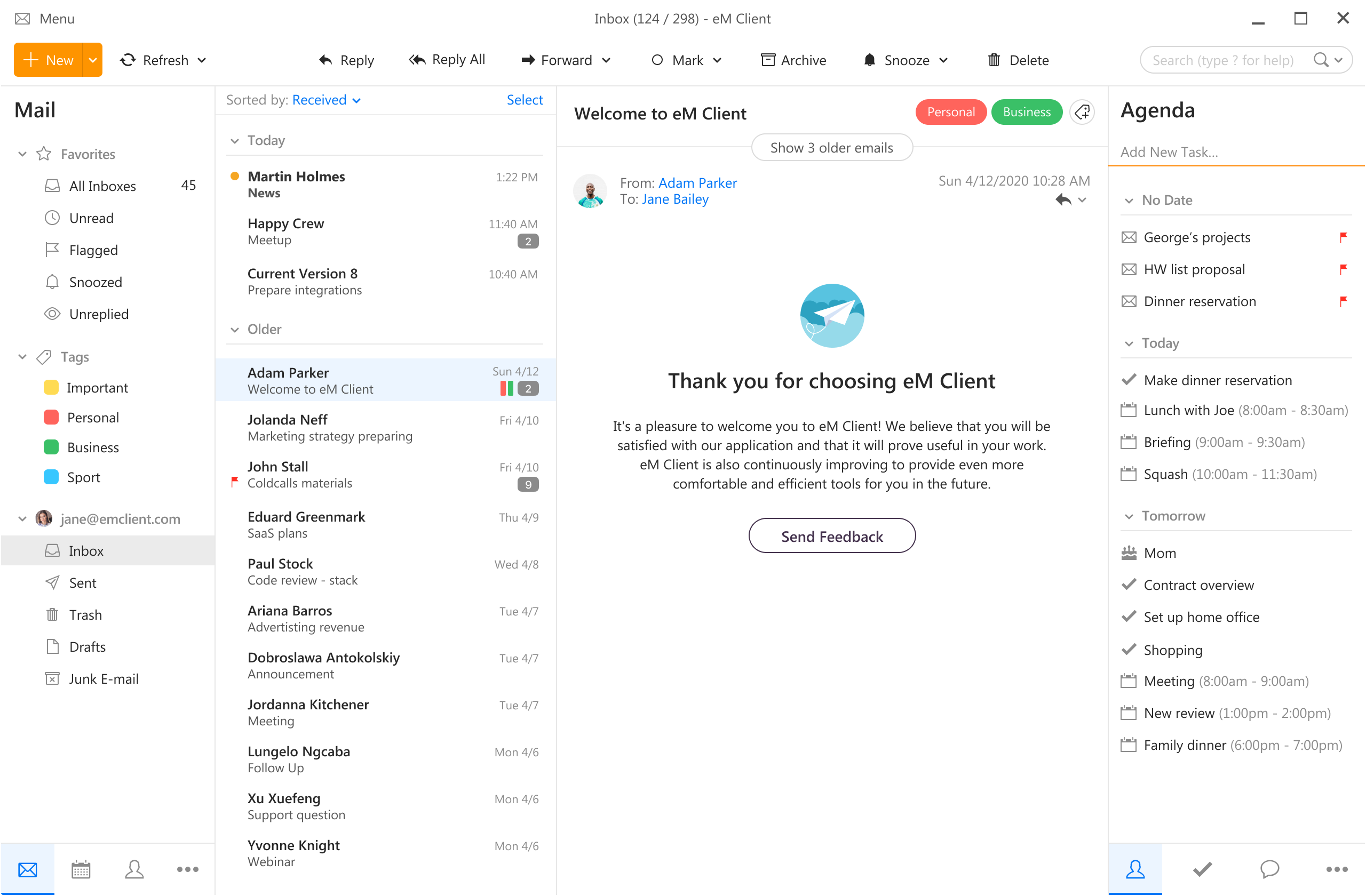
eM Client offers a wide array of features, including a calendar, contacts, and chat. Support is provided for all the major email services including Gmail, Yahoo, iCloud, and Outlook.com. The latest version also offers PGP encryption, live backup, basic image editing capabilities, and auto-replies for Gmail.
Its automatic system makes it very easy to get emails from other services since there is no manual setting, all that is needed is to type in your email and eM Client will do everything else automatically.
A one-time purchase is not pricy and it could offer some features that some free clients are missing. Go check it out with a free trial and see if it is for you.
Mailbird
https://www.getmailbird.com
This eMail client's main focus is the simplicity of use with visual appeal while tackling multiple eMail accounts. It has many built-in apps along with a customizable interface. Unlike some more Microsoft-centric email clients, Mailbird Business supports a diverse range of integrated apps, including WhatsApp, Google Docs, Google Calendar, Facebook, Twitter, Dropbox, and Slack, all making for a better-streamlined workflow.
The downside of this client is the yearly subscription plan. I think people, in general, want to get away from software subscription plans so I will include this as a downside but bear in mind it is downside just in terms of a business plan not in the client itself.
Inky
https://www.inky.com/
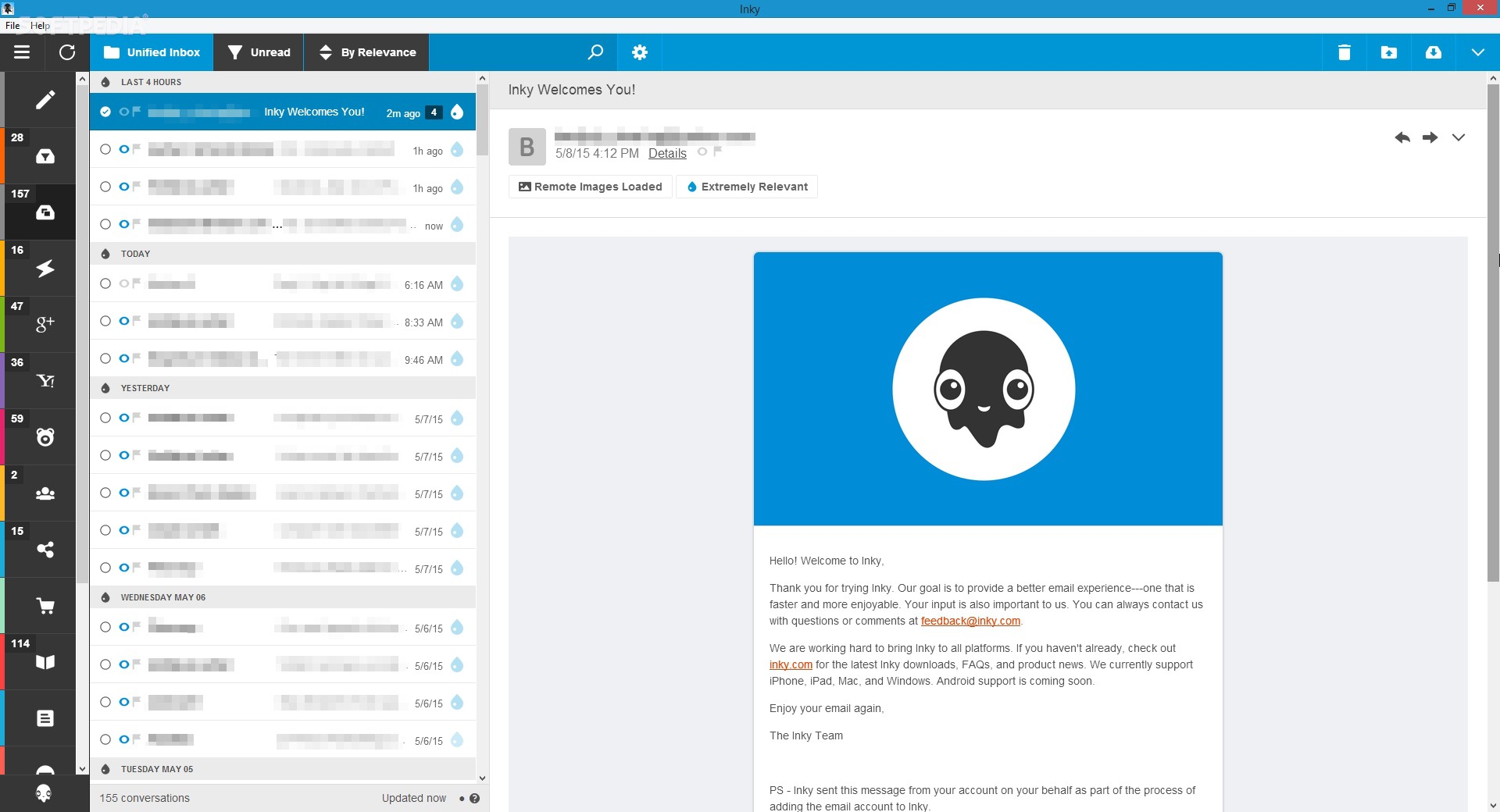
Inky is eMail client if you are looking for security. It uses AI along with machine learning in order to block all types of phishing attacks that can get through to other clients. The proprietary machine learning technology can literally read an email to determine if it has phishing content, and then is able to quarantine the email or deliver it with the malicious links disabled. It also takes things a step further and offers an analytics dashboard, which allows an administrator to see patterns of attacks based on dates, or targeted users.
The downside is that client itself is so much focused on security that sometimes some nonsecurity features get overlooked and provide a poor experience but if you need a good and greatly secured eMail client Inky is one to check out.

 It would be very difficult to even start a free eMail list without mentioning Google's Gmail. Introduced all the way back in 2004 as an invite-only service it became over time the most popular email platform largely due to the fact Google is offering free eMail accounts.
There are a lot of good things to be said about Gmail itself, most of the area is clutter-free and the largest space is reserved for eMail itself letting users focus on what is important. WEB client itself means that you do not need to have any application installed on your device, altho via Google chrome, you can use Gmail offline offering you flexibility if needed.
The ability to connect and manage other accounts like Outlook, Yahoo, etc is just making Gmail even more attractive, and the snooze feature is a really neat little detail that will pause eMail notifications if you need to focus on other things.
Lack of organizing messages into folders is a little confusing since Gmail offers its own unique label system but sometimes I need to have old reliable save eMail to folder.
All in all, Gmail is a great service and it offers a great eMail on the go experience.
It would be very difficult to even start a free eMail list without mentioning Google's Gmail. Introduced all the way back in 2004 as an invite-only service it became over time the most popular email platform largely due to the fact Google is offering free eMail accounts.
There are a lot of good things to be said about Gmail itself, most of the area is clutter-free and the largest space is reserved for eMail itself letting users focus on what is important. WEB client itself means that you do not need to have any application installed on your device, altho via Google chrome, you can use Gmail offline offering you flexibility if needed.
The ability to connect and manage other accounts like Outlook, Yahoo, etc is just making Gmail even more attractive, and the snooze feature is a really neat little detail that will pause eMail notifications if you need to focus on other things.
Lack of organizing messages into folders is a little confusing since Gmail offers its own unique label system but sometimes I need to have old reliable save eMail to folder.
All in all, Gmail is a great service and it offers a great eMail on the go experience.
 Free Windows eMail client simply called Mail is what was once outlook express. Mail itself has the ability to work with other popular accounts like Google Gmail account, Yahoo, iCloud etc. How it comes with Windows OS and it integrates very well with Microsoft Calendar, this eMail client is for many the first choice.
On the negative side, I might say this is a strip-down version of Outlook which is paid solution so some features are missing if we would compare the two.
Overall, a simple and nice eMail client worth your time, especially if you are on the Windows platform.
Free Windows eMail client simply called Mail is what was once outlook express. Mail itself has the ability to work with other popular accounts like Google Gmail account, Yahoo, iCloud etc. How it comes with Windows OS and it integrates very well with Microsoft Calendar, this eMail client is for many the first choice.
On the negative side, I might say this is a strip-down version of Outlook which is paid solution so some features are missing if we would compare the two.
Overall, a simple and nice eMail client worth your time, especially if you are on the Windows platform.
 Great eMail client matching in functions against paid and premium solutions of big tech companies. Fueled with plenty of customization options and reskinning ones this eMail client offers a lot for its free price tag.
It is also fueled by Mozilla community focusing on privacy and security. It can work with any mail service and it is lightweight with a clean look, altho the look itself can be heavily customized.
The bad side is that client itself relies on email services to provide cloud-based emails, so if you are receiving your email via a service that does not have a cloud-based service in itself all of your received emails will be locked to the computer where you have received them. Also customizing it can be sometimes a little too technical for the average computer user.
All in all, Thunderbird is one great eMail client and it would be a shame not to use it because of its technical side, if you need a reliable and secure eMail client on a single machine, look no further than Thunderbird.
Great eMail client matching in functions against paid and premium solutions of big tech companies. Fueled with plenty of customization options and reskinning ones this eMail client offers a lot for its free price tag.
It is also fueled by Mozilla community focusing on privacy and security. It can work with any mail service and it is lightweight with a clean look, altho the look itself can be heavily customized.
The bad side is that client itself relies on email services to provide cloud-based emails, so if you are receiving your email via a service that does not have a cloud-based service in itself all of your received emails will be locked to the computer where you have received them. Also customizing it can be sometimes a little too technical for the average computer user.
All in all, Thunderbird is one great eMail client and it would be a shame not to use it because of its technical side, if you need a reliable and secure eMail client on a single machine, look no further than Thunderbird.
 Outlook comes as a part of the Microsoft Office suite and as one of the oldest eMail clients, it is still widely popular and adopted through many users and businesses. It has tight integration with all Microsoft services and full integration with Calendar making it one of the if not the best eMail client out there.
Outlook also has a free online service completely free for personal use as well.
The downside is that you can not get it as a separate product if you want a business version other than as a part of the Office suite.
The final verdict would be that this is perhaps the best eMail client out but the big downside is that there is no desktop version outside the Office suite.
Outlook comes as a part of the Microsoft Office suite and as one of the oldest eMail clients, it is still widely popular and adopted through many users and businesses. It has tight integration with all Microsoft services and full integration with Calendar making it one of the if not the best eMail client out there.
Outlook also has a free online service completely free for personal use as well.
The downside is that you can not get it as a separate product if you want a business version other than as a part of the Office suite.
The final verdict would be that this is perhaps the best eMail client out but the big downside is that there is no desktop version outside the Office suite.
 eM Client offers a wide array of features, including a calendar, contacts, and chat. Support is provided for all the major email services including Gmail, Yahoo, iCloud, and Outlook.com. The latest version also offers PGP encryption, live backup, basic image editing capabilities, and auto-replies for Gmail.
Its automatic system makes it very easy to get emails from other services since there is no manual setting, all that is needed is to type in your email and eM Client will do everything else automatically.
A one-time purchase is not pricy and it could offer some features that some free clients are missing. Go check it out with a free trial and see if it is for you.
eM Client offers a wide array of features, including a calendar, contacts, and chat. Support is provided for all the major email services including Gmail, Yahoo, iCloud, and Outlook.com. The latest version also offers PGP encryption, live backup, basic image editing capabilities, and auto-replies for Gmail.
Its automatic system makes it very easy to get emails from other services since there is no manual setting, all that is needed is to type in your email and eM Client will do everything else automatically.
A one-time purchase is not pricy and it could offer some features that some free clients are missing. Go check it out with a free trial and see if it is for you.
 This eMail client's main focus is the simplicity of use with visual appeal while tackling multiple eMail accounts. It has many built-in apps along with a customizable interface. Unlike some more Microsoft-centric email clients, Mailbird Business supports a diverse range of integrated apps, including WhatsApp, Google Docs, Google Calendar, Facebook, Twitter, Dropbox, and Slack, all making for a better-streamlined workflow.
The downside of this client is the yearly subscription plan. I think people, in general, want to get away from software subscription plans so I will include this as a downside but bear in mind it is downside just in terms of a business plan not in the client itself.
This eMail client's main focus is the simplicity of use with visual appeal while tackling multiple eMail accounts. It has many built-in apps along with a customizable interface. Unlike some more Microsoft-centric email clients, Mailbird Business supports a diverse range of integrated apps, including WhatsApp, Google Docs, Google Calendar, Facebook, Twitter, Dropbox, and Slack, all making for a better-streamlined workflow.
The downside of this client is the yearly subscription plan. I think people, in general, want to get away from software subscription plans so I will include this as a downside but bear in mind it is downside just in terms of a business plan not in the client itself.
 Inky is eMail client if you are looking for security. It uses AI along with machine learning in order to block all types of phishing attacks that can get through to other clients. The proprietary machine learning technology can literally read an email to determine if it has phishing content, and then is able to quarantine the email or deliver it with the malicious links disabled. It also takes things a step further and offers an analytics dashboard, which allows an administrator to see patterns of attacks based on dates, or targeted users.
The downside is that client itself is so much focused on security that sometimes some nonsecurity features get overlooked and provide a poor experience but if you need a good and greatly secured eMail client Inky is one to check out.
Inky is eMail client if you are looking for security. It uses AI along with machine learning in order to block all types of phishing attacks that can get through to other clients. The proprietary machine learning technology can literally read an email to determine if it has phishing content, and then is able to quarantine the email or deliver it with the malicious links disabled. It also takes things a step further and offers an analytics dashboard, which allows an administrator to see patterns of attacks based on dates, or targeted users.
The downside is that client itself is so much focused on security that sometimes some nonsecurity features get overlooked and provide a poor experience but if you need a good and greatly secured eMail client Inky is one to check out.